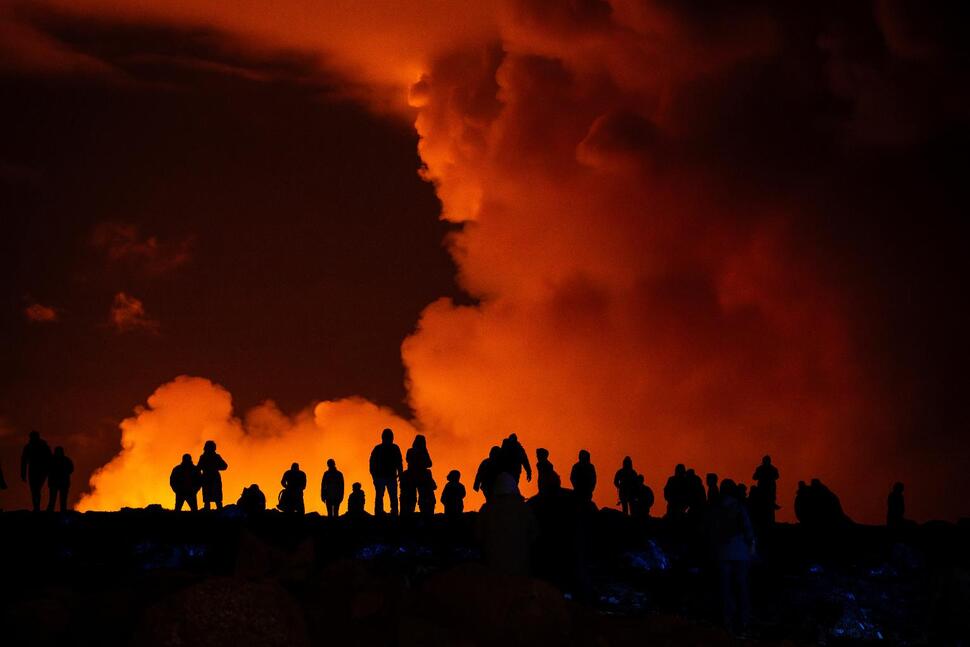
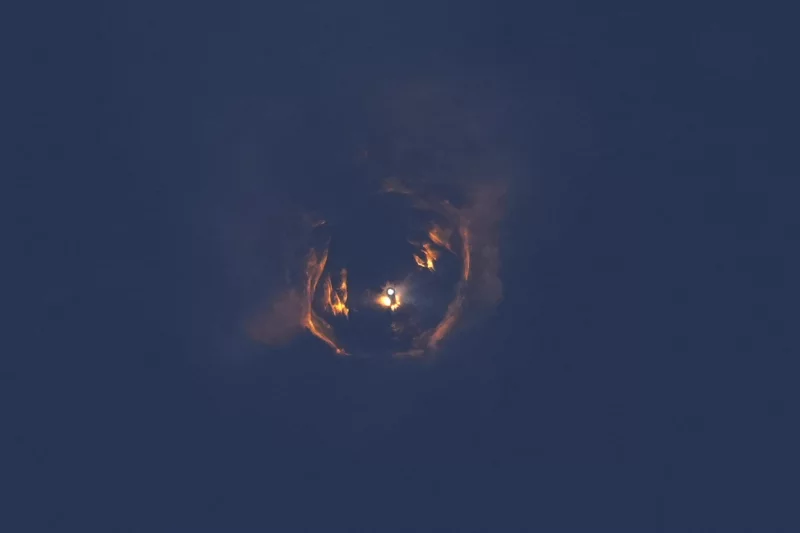
For the fourth time in three months, sending orange jets of lava into the night sky, a volcano in Iceland erupted on the evening of Saturday, March 16, 2024. Iceland’s Meteorological Office said the eruption opened a fissure in the earth about 3 kilometers (almost 2 miles) long between Stóra-Skógfell and Hagafell mountains on the Reykjanes Peninsula. The Met Office had warned for weeks that the magma, molten rock, and lava were accumulating over time making an eruption imminent. The eruption site is a few kilometers (miles) northeast of Grindavik, a coastal town of 3,800 people about 50 kilometers (30 miles) southwest of Iceland’s capital, Reykjavik, that was evacuated before the initial eruption in December. A few residents who had returned to their homes were evacuated again Saturday.
The volcano eventually erupted on December 18th, sending lava flowing away from Grindavik. A second eruption that began on January 14th sent lava toward the town. Defensive walls that had been bolstered after the first eruption stopped some of the flow, but several buildings were consumed by the lava. Both eruptions lasted only a matter of days. A third eruption began on February 8th. It petered out within hours, but not before a river of lava engulfed a pipeline, cutting off heat and hot water to thousands of people. RUV quoted geophysicist Magnús Tumi Guðmundsson as saying that the latest eruption is the most powerful so far. The Met Office said some of the lava was flowing towards the defensive barriers around Grindavik.
Hundreds of people were evacuated from the Blue Lagoon thermal spa when the eruption began, one of Iceland’s top tourist attractions, national broadcaster RUV said. No flight disruptions were reported at nearby Keflavik, Iceland’s main airport. No confirmed deaths have been reported from any of the recent eruptions, but a workman was declared missing after falling into a fissure opened by the volcano. Iceland, which sits above a volcanic hot spot in the North Atlantic, sees regular eruptions and is highly experienced at dealing with them. The most disruptive in recent times was the 2010 eruption of the Eyjafjallajokull volcano, which spewed huge clouds of ash into the atmosphere and led to widespread airspace closures over Europe.